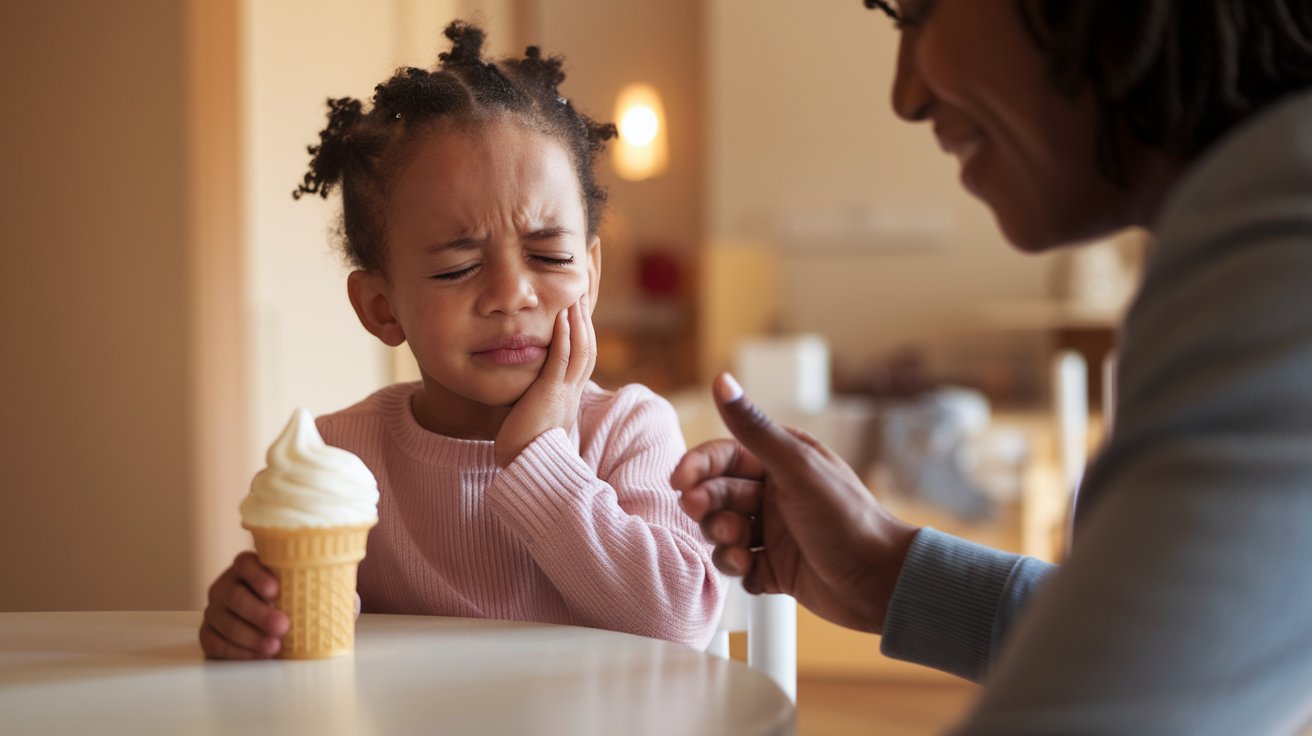
Common Causes of Tooth Sensitivity in Children and How to Treat It
Tooth sensitivity is a common dental issue that can cause discomfort or pain when consuming hot, cold, sweet, or acidic foods and drinks. While many people associate tooth sensitivity with adults, it’s not uncommon for children to experience it as well. As a parent, it’s important to understand the possible causes of tooth sensitivity in your child and know the steps you can take to treat and prevent it.
What is Tooth Sensitivity?
Tooth sensitivity occurs when the protective enamel layer on a tooth wears down, exposing the underlying dentin. The dentin contains microscopic tubules that connect to the tooth’s nerve. When stimuli such as temperature changes or sweet foods come in contact with these tubules, it can lead to pain or discomfort. Children may express this discomfort by avoiding certain foods or complaining of sharp pain when brushing or eating.
Common Causes of Tooth Sensitivity in Children
Several factors can contribute to tooth sensitivity in children, ranging from poor dental habits to medical conditions. Below are some of the most common causes:
1. Enamel Erosion
Enamel, the outermost layer of a tooth, acts as a protective shield for the softer layers beneath. In children, enamel erosion is one of the leading causes of tooth sensitivity. Enamel can wear away due to:
- Acidic Foods and Drinks: Frequent consumption of sugary or acidic foods and beverages like soda, candy, and citrus fruits can erode the enamel.
- Brushing Too Hard: Some children may apply too much pressure when brushing their teeth, causing enamel to wear away over time.
- Acid Reflux: If your child experiences acid reflux, stomach acids can make their way into the mouth, eroding enamel and leading to tooth sensitivity.
2. Tooth Decay and Cavities
Tooth decay is a significant cause of sensitivity in children. When bacteria in the mouth feed on sugars, they produce acids that erode the enamel and create cavities. Once a cavity forms, it exposes the dentin layer and can lead to sensitivity when eating or drinking.
3. New Tooth Eruption
When children are in the stage of losing baby teeth and getting their permanent teeth, sensitivity can arise as the new teeth come in. This is a natural process, but the exposed dentin during the eruption can cause discomfort.
4. Gum Disease
Children are not immune to gum disease. Gingivitis, the early stage of gum disease, can cause gum recession, which exposes the tooth’s root. The root is more sensitive than the crown of the tooth because it lacks a protective enamel layer. As a result, children may experience sensitivity near the gumline.
5. Teeth Grinding (Bruxism)
Some children grind their teeth, especially at night. This habit, known as bruxism, can wear down the enamel over time, leading to tooth sensitivity. You may notice your child grinding their teeth while sleeping, or they may complain of sore jaw muscles in the morning.
6. Dental Procedures
Certain dental treatments, such as fillings, crowns, or orthodontic adjustments, can lead to temporary sensitivity. This is typically short-lived and resolves once the tooth adjusts to the procedure.
7. Orthodontic Treatments
If your child is undergoing orthodontic treatment such as braces, they may experience tooth sensitivity. This can happen as the teeth shift into new positions, putting pressure on certain teeth and making them more sensitive.
Signs and Symptoms of Tooth Sensitivity in Children
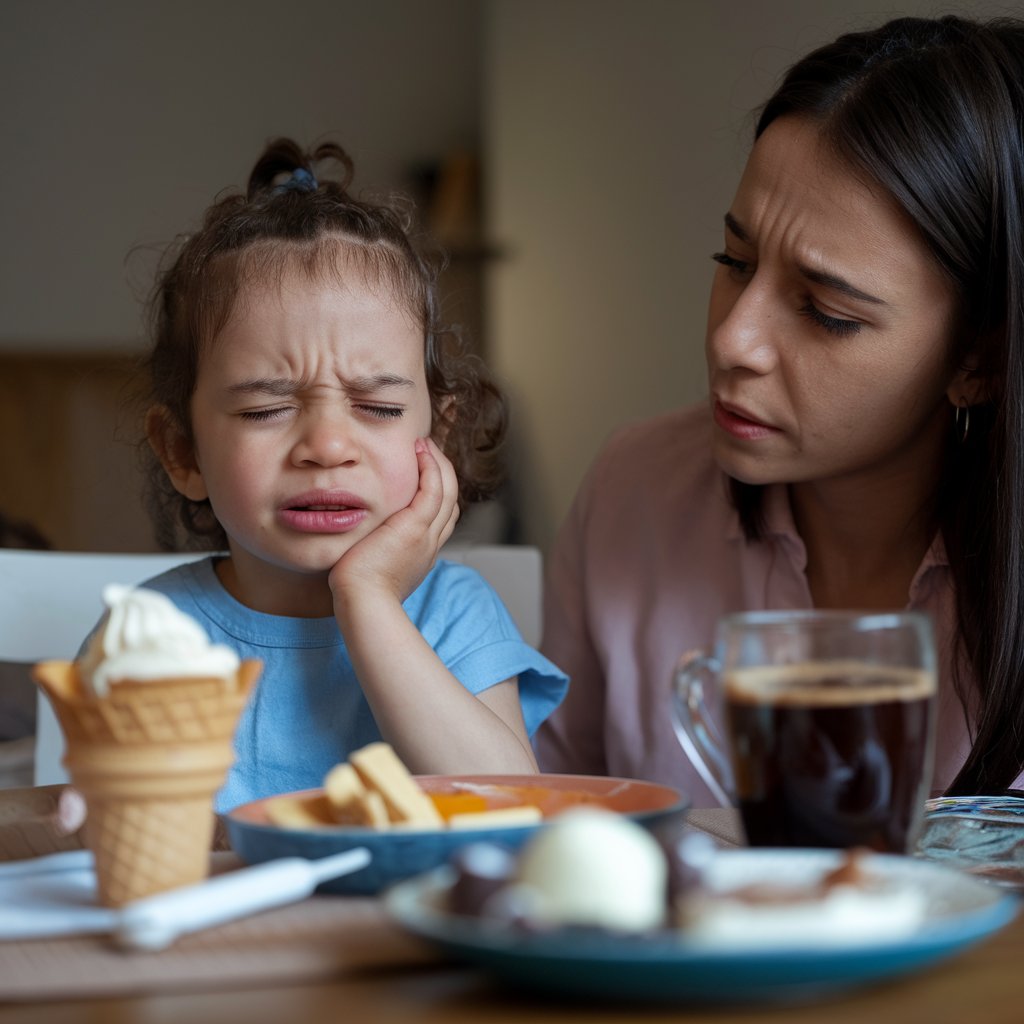

As a parent, it can sometimes be difficult to tell if your child is experiencing tooth sensitivity. Here are some signs that may indicate an issue:
- Complaints of pain when eating or drinking hot, cold, or sweet foods.
- Avoiding certain foods that they used to enjoy.
- Complaining of discomfort while brushing their teeth.
- Frequent rubbing of their jaw or face after eating.
important to consult a pediatric dentist to determine the cause and get appropriate treatment.
How to Treat Tooth Sensitivity in Children
Once you’ve identified that your child is suffering from tooth sensitivity, there are several treatment options available. The right approach will depend on the underlying cause, but here are some common treatment strategies:
1. Use of Desensitizing Toothpaste
Desensitizing toothpaste is specifically formulated to reduce tooth sensitivity. These toothpastes contain compounds that help block the transmission of sensations from the tooth surface to the nerve. Encourage your child to use this type of toothpaste as part of their regular brushing routine.
2. Improve Brushing Techniques
Teach your child to use gentle circular motions when brushing their teeth. Using a soft-bristled toothbrush can also help prevent enamel erosion caused by aggressive brushing. Supervise young children while they brush to ensure they are using the correct technique.
3. Maintain a Healthy Diet
Limiting your child’s consumption of acidic and sugary foods and beverages can protect their enamel and reduce the risk of tooth sensitivity. Encourage a balanced diet with plenty of vegetables, fruits, and water, which promote overall oral health.
4. Fluoride Treatments
Fluoride helps to strengthen enamel and can reduce sensitivity. Your child’s dentist may recommend fluoride treatments during regular dental visits to help protect their teeth. You can also ask about fluoride-enriched toothpaste or mouth rinses to use at home.
5. Sealants
For children with particularly sensitive teeth, dental sealants can be a great option. A sealant is a protective coating applied to the chewing surfaces of the teeth to prevent decay and shield the enamel. Sealants can act as a barrier against sensitivity triggers.
6. Mouthguards for Teeth Grinding
If your child grinds their teeth at night, a custom-made mouthguard can protect their enamel from further wear and prevent sensitivity. The mouthguard provides a cushion between the upper and lower teeth, reducing the damage caused by grinding.
7. Addressing Gum Disease
If gum disease is the root cause of your child’s tooth sensitivity, early treatment is key. Regular dental checkups, good oral hygiene habits, and professional cleanings can help prevent and treat gum disease. In more severe cases, your child’s dentist may recommend specialized treatments to restore gum health.
8. Dental Restoration for Cavities
If tooth decay is causing the sensitivity, your child will likely need a dental filling to treat the cavity. This will prevent further damage to the tooth and alleviate the discomfort caused by exposed dentin.
Preventing Tooth Sensitivity in the Future
Prevention is always better than cure. Here are some tips to help protect your child’s teeth from sensitivity:
- Encourage good oral hygiene: Brushing twice a day with fluoride toothpaste and flossing daily can help keep tooth decay and gum disease at bay.
- Regular dental visits: Make sure your child sees the dentist every six months for a cleaning and checkup.
- Monitor your child’s diet: Limiting sugary snacks and acidic drinks will help protect their enamel.
- Educate your child: Teach your child about the importance of proper dental care and the impact of diet on their teeth.
When to See a Dentist
If your child is experiencing ongoing tooth sensitivity, it’s important to see a pediatric dentist to rule out any serious issues such as cavities or gum disease. A dentist can perform an examination and recommend appropriate treatments to alleviate discomfort and prevent further damage.
Tooth sensitivity can be uncomfortable for children, but it’s often manageable with proper care. By understanding the common causes of tooth sensitivity, such as enamel erosion, cavities, and gum disease, and knowing the available treatments, you can help your child maintain healthy, pain-free teeth. Regular dental checkups, a balanced diet, and good oral hygiene habits are essential in preventing tooth sensitivity and ensuring your child’s long-term oral health. If your child is showing signs of sensitivity, don’t hesitate to consult your pediatric dentist for personalized advice and treatment options.
 Call
Call